How Long Does It Take in Pokemon Sun and Moon to Change From Day to Night and to Day Again

SkyTellers Moon Phases activities for immature children
See likewise:
Explore Marvel Moon activities and resources
Middle school Moon Phases activities and resource
LPI Family Upshot Moon activities and resources
Nigh Our Moon
A moon is a natural satellite of a planetary body. It revolves around that trunk — a planet or asteroid. Our Moon is the merely natural satellite of Earth.
Why does our Moon polish?
The moon "shines" because it reflects the Sun's light. At times, our Moon reflects and then much light that information technology makes viewing parts of the night sky challenging!
Why does our Moon'due south shape change?

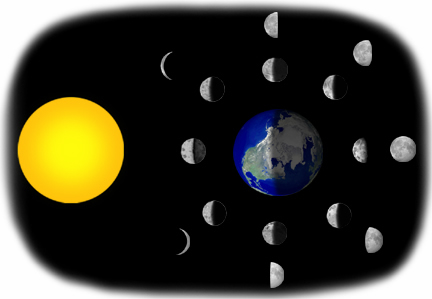
Our Moon's shape doesn't actually change — information technology only appears that fashion! The "amount" of Moon that we meet as we expect from Earth changes in a cycle that repeats well-nigh one time a calendar month (29.5 days). The relative positions of our Dominicus, World, and Moon, cause these changes.
As our Moon orbits around Globe, the side facing the Sun is always illuminated, just like Globe's daylight side is illuminated by the Dominicus.
What nosotros meet from Earth, yet, is a different story. Starting with the dark new Moon, we come across the low-cal part of the Moon "grow" from a sliver to a one-half to a total Moon — then the illuminated part decreases, becoming thinner until there is no visible Moon in the sky and we are at the new Moon part of the cycle once again.
We accept a "new Moon" when our Moon'southward orbit effectually Earth moves it between World and the Sun. From Earth, the Moon's surface looks dark because the illuminated side is facing away from World. Every bit our Moon continues its orbit counterclockwise around Globe (viewed from above the north pole), more than and more of the illuminated part of the Moon becomes visible to us, until it reaches the "total Moon" stage. A full Moon occurs when the Moon has moved in its orbit so that Earth is "between" the Moon and the Sun.
Between the new and full Moon, the amount of Moon nosotros run across grows — or waxes from its correct side toward its left side. As it passes the total Moon stage, the amount of illumination decreases — or wanes — from correct to left. Finally, the Moon returns to its position between the World and the Sun, and on Earth we detect the new Moon again.
In the southern hemisphere, illumination of the Moon increases from the left to the right side in the waxing stage and the dark part increases in coverage from left to right in the waning phase, which is opposite of the northern hemisphere. No matter where on Globe an observer is, however, the phases of the Moon occur at the aforementioned time.
What causes a lunar eclipse?
Pictures of the Moon's phases often arrive await like there should be a lunar eclipse during each full Moon and a solar eclipse during each new Moon. Even so, ii things have to happen for a full lunar eclipse. Beginning, the Moon has to exist total, so there is just an opportunity for a lunar eclipse about once each month. Second, the Moon has to pass through World's shadow. The Moon'southward orbit around Earth is tilted a little, or "off kilter" past nigh v degrees to the Earth'south orbit around the Lord's day. This means that most of the time the Moon is slightly above or beneath Earth's plane of orbit — and out of the shadow bandage by Globe where information technology blocks the Sun'south lite. No eclipse occurs during these full Moons. But two to four times each twelvemonth, a total Moon occurs when the Moon's orbit intersects Earth'due south plane of orbit, placing the Moon in Globe's shadow — and a lunar eclipse occurs!
How long does it accept our Moon to go around World?
It takes 27 days, vii hours, and 43 minutes for our Moon to complete i total orbit effectually Earth. This is called the sidereal month, and is measured past our Moon'south position relative to distant "fixed" stars. However, it takes our Moon about 29.5 days to consummate i cycle of phases (from new Moon to new Moon). This is chosen the synodic month. The difference betwixt the sidereal and synodic months occurs considering as our Moon moves effectually World, the Earth as well moves around our Dominicus. Our Moon must travel a trivial farther in its path to make upwards for the added altitude and consummate the phase cycle.
What is the nighttime side of the Moon?
In spite of the phrase, at that place actually is no dark side of the Moon! Only similar Earth, our Moon rotates on its own axis and experiences daylight and nighttime cycles. Our Moon'southward day and night cycles are a little longer than Earth's — the Moon spins on its axis once every 27.3 days. Our Moon'south period of rotation matches the time of revolution effectually Earth. In other words, it takes our Moon the same length of time to plough once on its axis equally it takes information technology to get one time completely around the Earth! This ways that Earth observers always encounter the same side of the Moon (called the "nearside"). The side we do not see from Earth, chosen the "farside," has been mapped during lunar missions.

Nearside view of World's Moon as seen past the Galileo Spacecraft

Farside view of World'southward Moon as seen
Do other planets have moons?
Yes! Several of the planets in our solar system accept natural satellites that orbit them. Some are so recently discovered that they have non yet been named. Mars has Phobos and Deimos, ii small moons that circle very close to the martian surface. Jupiter has more known satellites than any other planet — 61! The astronomer Galileo reported Jupiter'southward largest moons — Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto — in 1610. Saturn has at to the lowest degree 31 satellites, Uranus has 27, and Neptune has 13 — and more are being discovered all the fourth dimension! Pluto has one moon — Charon — the largest moon with respect to the size of the planet information technology revolves around. Only Mercury and Venus do not have any known satellites. Satellites are not restricted to planets; tiny Dactyl was discovered orbiting the asteroid Ida in 1994!

Simulated color view of Saturn'south moon Epimetheus

Jupiter'southward moon Europa
Jupiter's moon Io
Mars' moon Phobos
Source: https://www.lpi.usra.edu/education/skytellers/moon-phases/#:~:text=However%2C%20it%20takes%20our%20Moon,new%20Moon%20to%20new%20Moon).
0 Response to "How Long Does It Take in Pokemon Sun and Moon to Change From Day to Night and to Day Again"
Post a Comment